CHEP 2019 - Achieving metric oriented load balancing
Abstract
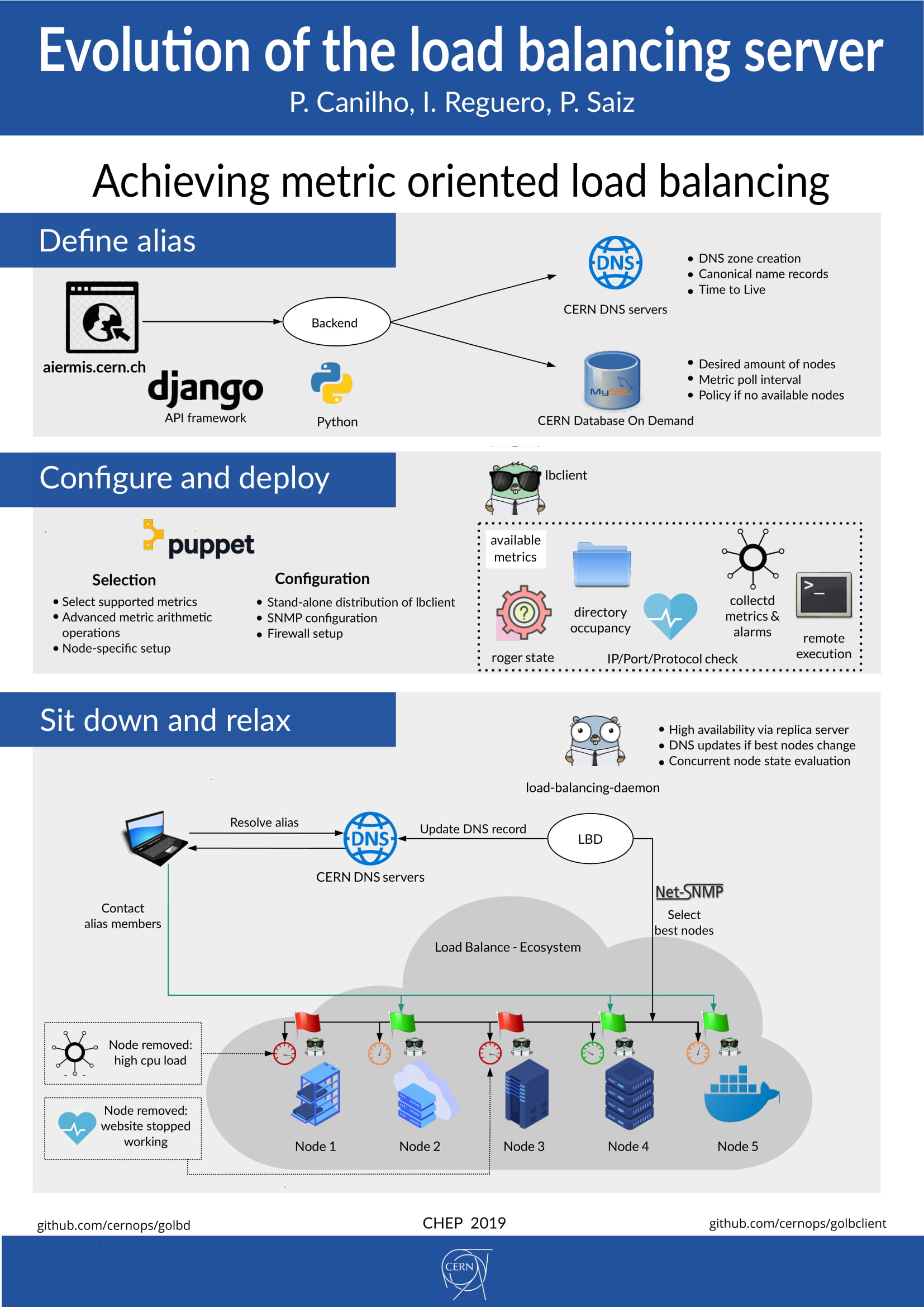
The Load Balance Service at CERN handles more that 400 aliases, distributed over more than 2000 nodes. After being in production for more than thirteen years, it has been going through a mayor redesign over the last two years. Last year, the server part got reimplemented in golang, taking advantage of the concurrency features offered by the language to improve the scaling of the system. This year, the client side and the communication between the client and the server have been the main focus. First of all, the client part of the Load Balance Service has been rewritten in golang. On top of that, it was evaluated to move from a model where the server probes the clients, to a model where the clients announce their states. This has a quite a lot of implications in the frequency of the updates, the security model and the deployment of the service. Finally, it was also evaluated to offer ‘HAProxy as a Service’, taking feedback on the client members using the same probes currently used for the DNS load balancing. All the components used by the Load Balance Service are open source, and they can be deployed at other places.